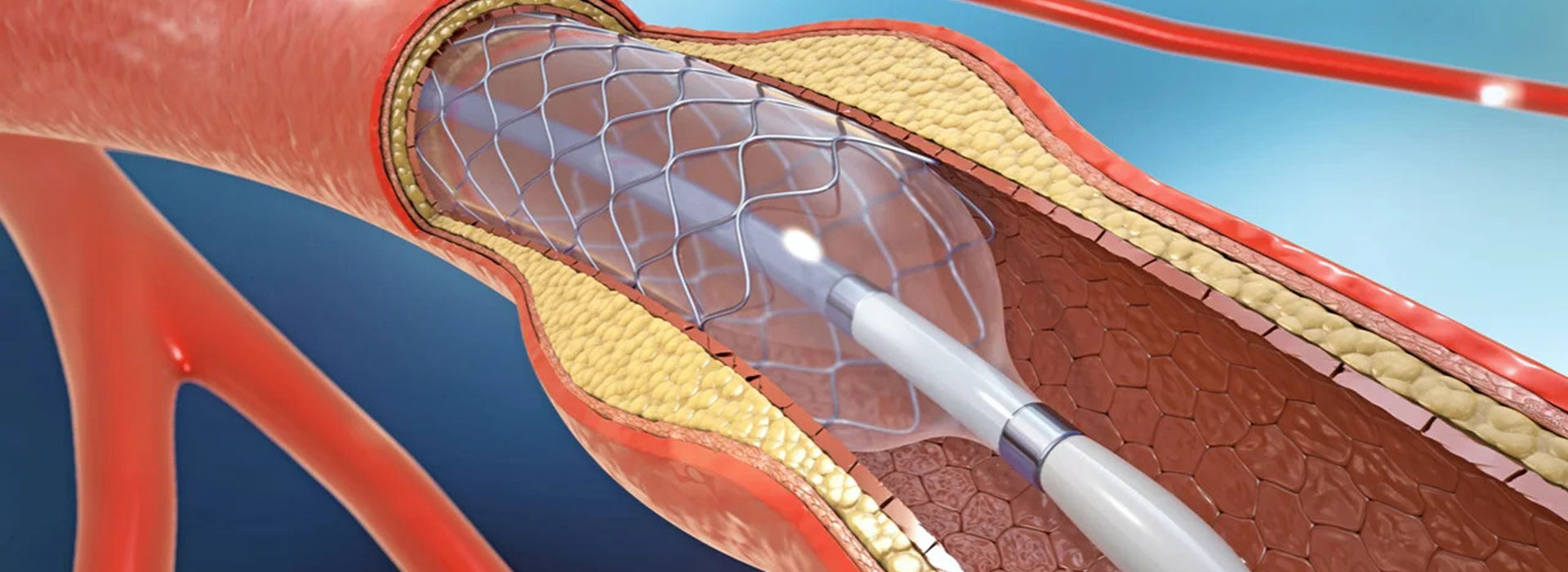
OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a newer imaging method similar to ultrasound, which uses infrared radiowaves (near-infrared light) instead of sound. It offers significantly better resolution, in particular the axial resolution of OCT is 10-15μm, i.e. ten times that of ultrasound.
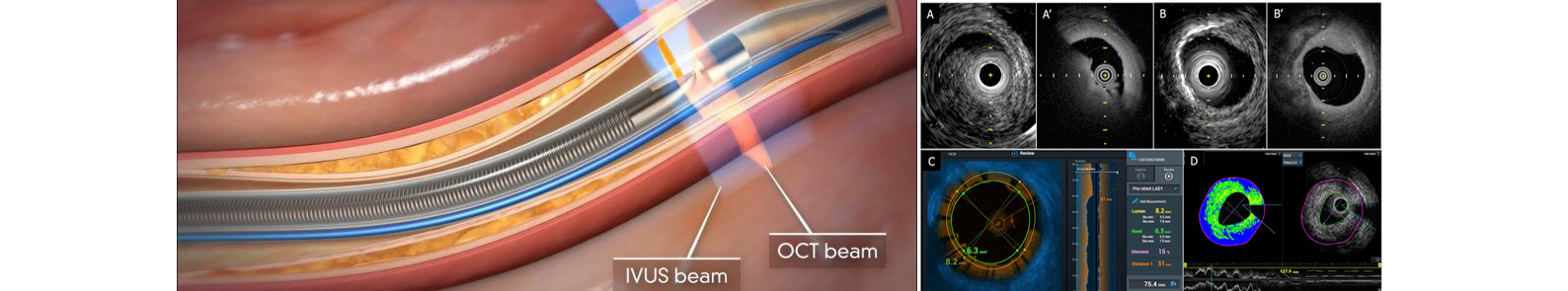
Due to its high resolution, OCT provides impressive images of vessel and atheromatous plaques similar to histology. It is an ideal method for the study of ambiguous lesions. OCT is also ideal for assessingstent restenosis and thrombosis mechanisms and for guiding angioplasty. With OCT elements such as stent tip separation, atherosclerotic plaque projection through the stent, proper or mal-appositioning of the stent and thrombus emerge more clearly and in higher percentages in relation with IVUS.


